Khi làm việc với Power Automate Desktop (PAD), chúng ta thường bị “mắc kẹt” hoặc phải tốn nhiều thời gian tìm các cách xử lý thay thế khi không có native actions hỗ trợ sẵn. Thông thường, vấn đề nằm ở cách bạn thao tác với các biến (variables) có trong flow.
Ví dụ: cách add/remove a column trong một data table đã tồn tại, cách tìm một item trong list khi item đó có thể xuất hiện nhiều lần và trả về index của nó, hoặc cách remove duplicate rows trong một data table…
Cách dễ nhất để xử lý các vấn đề này là sử dụng scripting actions. Tuy nhiên, điều này lại phát sinh thêm vấn đề:
- Nếu đoạn code đó được dùng ở nhiều nơi và bạn muốn sửa → phải sửa ở tất cả vị trí.
- Hoặc code của bạn chỉ chạy đúng một kịch bản, nhưng bạn hoàn toàn có thể chỉnh sửa để tái sử dụng cho kịch bản khác.
Bắt đầu từ PAD version 2.34, Microsoft đã hỗ trợ Custom Actions cho desktop flow. Tính năng này giúp tăng khả năng tái sử dụng, rút ngắn flow, và hỗ trợ đồng đồng nghiệp của chúng ta – những người làm low code – dễ dàng dùng lại các action.
Trong phần 1, tôi sẽ hướng dẫn nhanh cách tạo Custom Action.
1. Tải template để làm Custom Actions
Để bắt đầu, bạn có thể mở Package Manager Console và tải template được Microsoft cung cấp bằng câu lệnh:
dotnet new install Microsoft.PowerPlatform.PowerAutomate.Desktop.Actions.Templates
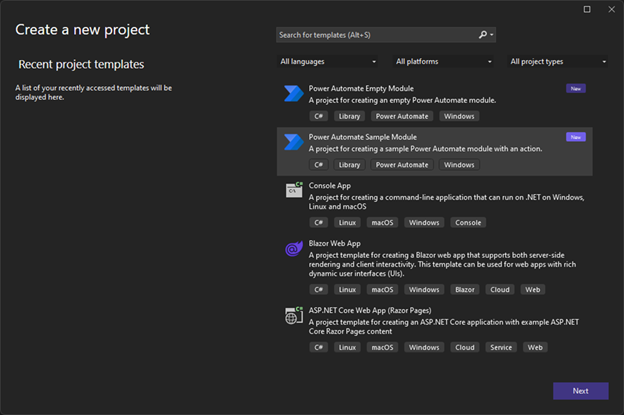
Ở đây tôi dùng Sample Module Template
2. Tạo Project
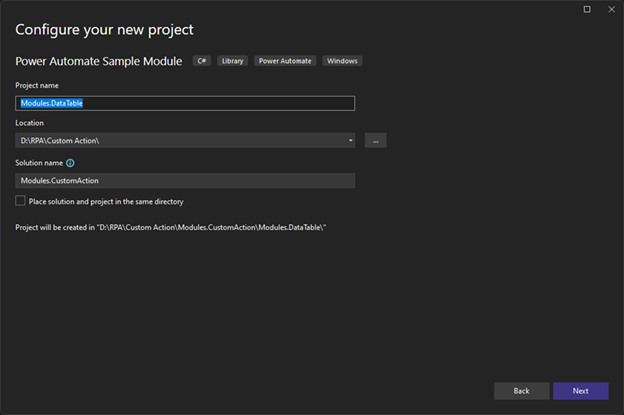
Tên Project bắt buộc phải tuân theo quy tắc sau nếu không sẽ bị lỗi “Module cache not found”:
?*.Modules.?*
Modules.?*
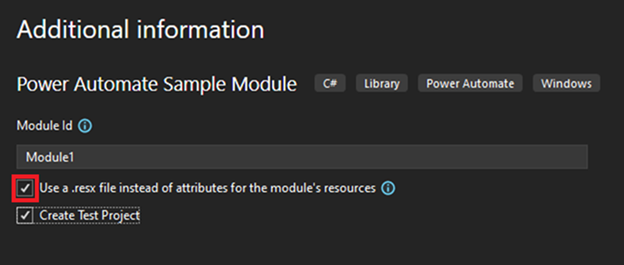
Bạn có thể tick chọn Use a .resx for setting metadata for Action và chọn thêm Test Project.
3. Coding
Trong ví dụ này, tôi sẽ tạo một Custom Action để add a column vào một data table đã tồn tại.
Đây là code mẫu:
using Microsoft.PowerPlatform.PowerAutomate.Desktop.Actions.SDK;
using Microsoft.PowerPlatform.PowerAutomate.Desktop.Actions.SDK.Attributes;
using System;
using System.Data;
namespace Modules.DataTable
{
[Action(Id = “AddColumnToDataTable”, FriendlyName = “Add column”, Order = 10, Description = “Add new column to data table”)]
[Throws(“ColumnExisted”, FriendlyName = “Column Existed”)] // TODO: change error name (or delete if not needed)
public class AddColumn : ActionBase
{
#region Properties
[InputArgument(Description = “Data table for add new column”, FriendlyName = “Data table”, Order = 1)]
public System.Data.DataTable dtDataTable { get; set; }
[InputArgument(Description = “New column to add into data table”, FriendlyName = “New column name”, Order = 2)]
public string strNewColumnName { get; set; }
[InputArgument(Description = “Default value to add into new column”, FriendlyName = “Default value”, Order = 3, Required = false)]
public string strDefaultValue { get; set; }
[OutputArgument(Order = 1, Description = “New Data table with new column added”)]
public System.Data.DataTable dtNewDataTable { get; set; }
#endregion
#region Methods Overrides
public override void Execute(ActionContext context)
{
try
{
//Add new column into Data table with strNewColumnName
dtDataTable.Columns.Add(strNewColumnName);
dtNewDataTable = dtDataTable.Copy();
//If strDefaultValue is not null, set default value for new column
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(strDefaultValue))
{
foreach (DataRow row in dtNewDataTable.Rows)
{
row[strNewColumnName] = strDefaultValue;
}
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
if (e is ActionException) throw;
throw new ActionException(“ColumnExisted”, e.Message, e.InnerException);
}
// TODO: set values to Output Arguments here
}
#endregion
}
}
4. Sign Custom Action
Đầu tiên, bạn phải tạo PowerShell script dùng để sign code file.
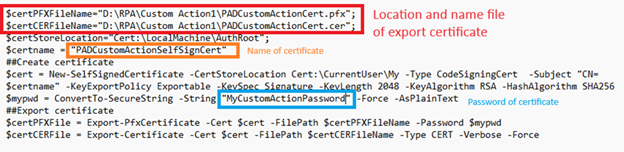
PowerShell script:
$certPFXFileName=”D:\RPA\Custom Action1\PADCustomActionCert.pfx”;
$certCERFileName=”D:\RPA\Custom Action1\PADCustomActionCert.cer”;
$certStoreLocation=”Cert:\LocalMachine\AuthRoot”;
$certname = “PADCustomActionSelfSignCert”
##Create certificate
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\CurrentUser\My -Type CodeSigningCert -Subject “CN=$certname” -KeyExportPolicy Exportable -KeySpec Signature -KeyLength 2048 -KeyAlgorithm RSA -HashAlgorithm SHA256
$mypwd = ConvertTo-SecureString -String “MyCustomActionPassword” -Force -AsPlainText
##Export certificate
$certPFXFile = Export-PfxCertificate -Cert $cert -FilePath $certPFXFileName -Password $mypwd
$certCERFile = Export-Certificate -Cert $cert -FilePath $certCERFileName -Type CERT -Verbose -Force
5. Build và Sign file DLL
Mở Command Prompt trong Visual Studio và thay đổi các parameter sau:
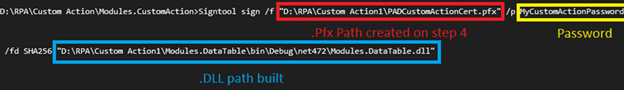
Signtool sign /f “D:\RPA\Custom Action1\PADCustomActionCert.pfx” /p MyCustomActionPassword /fd SHA256 “D:\RPA\Custom Action1\Modules.DataTable\bin\Debug\net472\Modules.DataTable.dll”
Fix lỗi “Signtool not recognize”:
- Download Windows Dev SDK:
https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/downloads/windows-sdk/ - Set Environment variable:
set PATH=”C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\bin\10.0.22621.0\x64\signtool.exe”;%PATH%
6. Tạo file .CAB
Tạo file .ps1 với nội dung sau để tạo file .CAB:
“param(
[ValidateScript({Test-Path $_ -PathType Container})]
[string]
$sourceDir,
[ValidateScript({Test-Path $_ -PathType Container})]
[string]
$cabOutputDir,
[string]
$cabFilename
)
$ddf = “”.OPTION EXPLICIT
.Set CabinetName1=$cabFilename
.Set DiskDirectory1=$cabOutputDir
.Set CompressionType=LZX
.Set Cabinet=on
.Set Compress=on
.Set CabinetFileCountThreshold=0
.Set FolderFileCountThreshold=0
.Set FolderSizeThreshold=0
.Set MaxCabinetSize=0
.Set MaxDiskFileCount=0
.Set MaxDiskSize=0
“”
$ddfpath = ($env:TEMP + “”\customModule.ddf””)
$sourceDirLength = $sourceDir.Length;
$ddf += (Get-ChildItem $sourceDir -Filter “”*.dll”” | Where-Object { (!$_.PSIsContainer) -and ($_.Name -ne “”Microsoft.PowerPlatform.PowerAutomate.Desktop.Actions.SDK.dll””) } | Select-Object -ExpandProperty FullName | ForEach-Object { ‘””‘ + $_ + ‘”” “”‘ + ($_.Substring($sourceDirLength)) + ‘””‘ }) -join “”`r`n””
$ddf | Out-File -Encoding UTF8 $ddfpath
makecab.exe /F $ddfpath
Remove-Item $ddfpath”
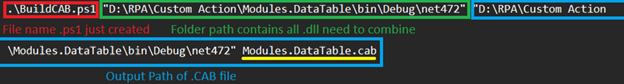
Ở đây tôi lưu file này với tên BuildCAB.ps1.
Sau đó mở PowerShell trong Visual Studio và thay đổi các parameter tương ứng.
.\BuildCAB.ps1 “D:\RPA\Custom Action1\Modules.DataTable\bin\Debug\net472” “D:\RPA\Custom Action1\Modules.DataTable\bin\Debug\net472” Modules.DataTable.cab
7. Sign file .CAB
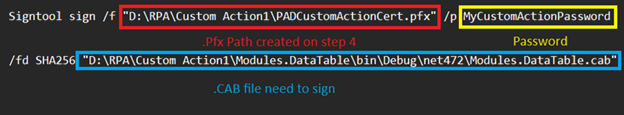
Mở lại Command Prompt ở bước 5 và thay đổi parameter để sign file .CAB.
Signtool sign /f “D:\RPA\Custom Action1\PADCustomActionCert.pfx” /p MyCustomActionPassword /fd SHA256 “D:\RPA\Custom Action1\Modules.DataTable\bin\Debug\net472\Modules.DataTable.cab”
8. Upload Custom Action lên Power Automate
- Truy cập Power Automate → Custom actions
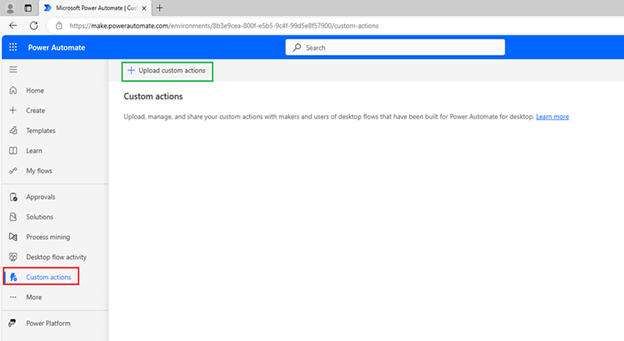
- Upload file .CAB
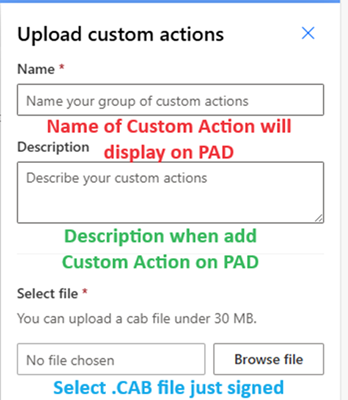
- Thêm Custom Action vào flow thông qua Asset Library
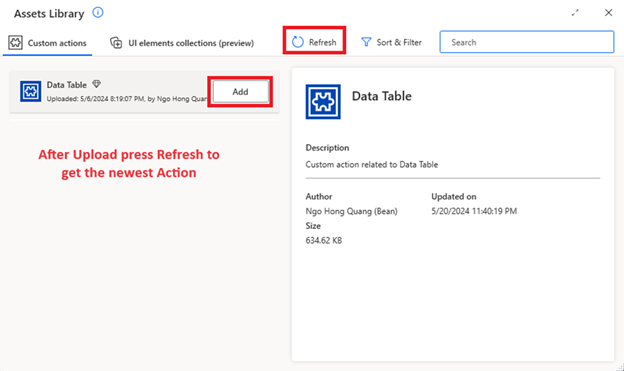
Cảm ơn bạn đã đọc. Hy vọng hướng dẫn này giúp bạn thao tác dễ dàng hơn trong việc tạo Custom Action.
Trong phần tiếp theo, tôi sẽ chia sẻ các lỗi thường gặp và cách khắc phục.